Building materials are the foundation of any construction project, and the strength and durability of these materials are critical to the safety and longevity of the structure. While many materials are commonly used in construction, some are weaker than others and may not be suitable for certain applications. In this article, we will explore the weakest building materials and their limitations, providing insights into the factors that influence material strength and durability.
What is the Weakest Building Material?
The weakest building material is a relative term, as the strength of a material depends on the application and the forces it will be subjected to. However, some materials are generally considered weaker than others, such as:
- Wood: While wood is a popular building material due to its availability and ease of use, it is relatively weak compared to other materials. Wood is susceptible to rot, decay, and insect damage, and it can warp or crack under stress.
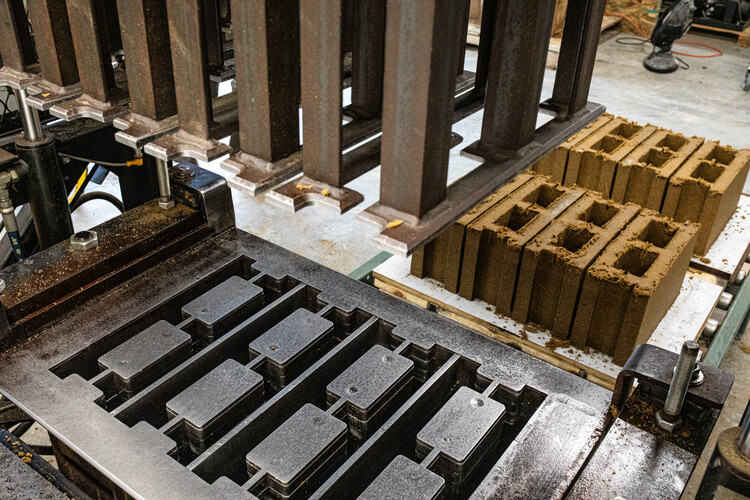
- Brick: Brick is a durable and fire-resistant material, but it is not as strong as concrete or steel. Brick is prone to cracking and crumbling under heavy loads or seismic activity.
- Plaster: Plaster is a common interior finishing material, but it is not suitable for load-bearing applications. Plaster is brittle and can crack or crumble under stress.
- Glass: Glass is a fragile material that is not suitable for load-bearing applications. While tempered glass is stronger than regular glass, it is still prone to shattering under impact.
Factors that Influence Material Strength and Durability:
The strength and durability of a building material depend on several factors, including:
- Composition: The chemical composition of a material can affect its strength and durability. For example, concrete is a strong and durable material due to its composition of cement, water, and aggregates.
- Manufacturing Process: The manufacturing process can also affect the strength and durability of a material. For example, steel that is heat-treated or tempered is stronger than untreated steel.
- Environmental Factors: Environmental factors such as moisture, temperature, and exposure to sunlight can affect the strength and durability of a material. For example, wood that is exposed to moisture can rot and decay, reducing its strength.
Conclusion:
Understanding the limitations of building materials is essential for ensuring the safety and longevity of a structure. While some materials may be weaker than others, they can still be suitable for certain applications if used correctly. By considering the factors that influence material strength and durability, builders can make informed decisions about which materials to use for their projects.